Every digital designer can at times run into the infamous issue of dealing with non-manifold edges. Whether it’s in Rhino or any other 3D software, this common but perplexing error has the potential to cause headaches and derail the progress of any modeling workflow.
Image: blenderartists.org
But fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a journey to delve into the intricacies of non-manifold edges and equip you with the knowledge and tools to tackle this issue head-on in Rhino. Let’s get our hands dirty and restore harmony to your 3D models!
What are Non-Manifold Edges?
In the geometric realm of 3D modeling, non-manifold edges are the troublemakers that disrupt the smooth flow of surfaces. They are essentially edges that do not cleanly belong to exactly two surfaces. Imagine a mathematical rebel, refusing to conform to the established order!
Non-manifold edges can arise from various modeling mishaps, such as overlapping faces, gaps between surfaces, or intersecting geometry. These rogue edges can lead to a plethora of downstream problems, including rendering artifacts, mesh deformation, and failed 3D prints.
Expert Insights: The Genesis of Non-Manifold Edges
To gain a deeper understanding of non-manifold edges, we sought the wisdom of Rhino expert, Dr. Adam Martin. According to Dr. Martin, “Non-manifold edges often originate from modeling shortcuts or careless geometry creation. When surfaces are not properly joined or trimmed, these problematic edges can sneak into your model.”
Preventing non-manifold edges in the first place is paramount. Dr. Martin advises, “Always strive for clean and precise geometry. Use proper modeling techniques, such as boolean operations with clean inputs, regular grids for subdivision, and avoiding overlapping faces.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing Non-Manifold Edges
If non-manifold edges have managed to infiltrate your model, fear not! Here’s a step-by-step guide to banish them from your digital realm:
- Identify the Miscreants: The first step is to identify the non-manifold edges lurking within your model. In Rhino, you can unveil these troublemakers using the “Analyze->Edge Tools->Non-Manifold Edges” command.
- Use the Explode Command: With the non-manifold edges exposed, proceed to “Explode” the problematic areas into individual surfaces. This action breaks down the complex geometry into its constituent parts.
- Trim and Join: Now armed with the knowledge of how your surfaces connect, it’s time for a cleanup. Trim away excess geometry from each surface, ensuring there are no overlaps or gaps. Subsequently, utilize the “Join” command to stitch them back together, creating clean and manifold edges.
- Run EdgeTools Again: After the surgical repair, re-run the “Analyze->Edge Tools->Non-Manifold Edges” command. This will verify if the healing process was a success or if further surgery is required.
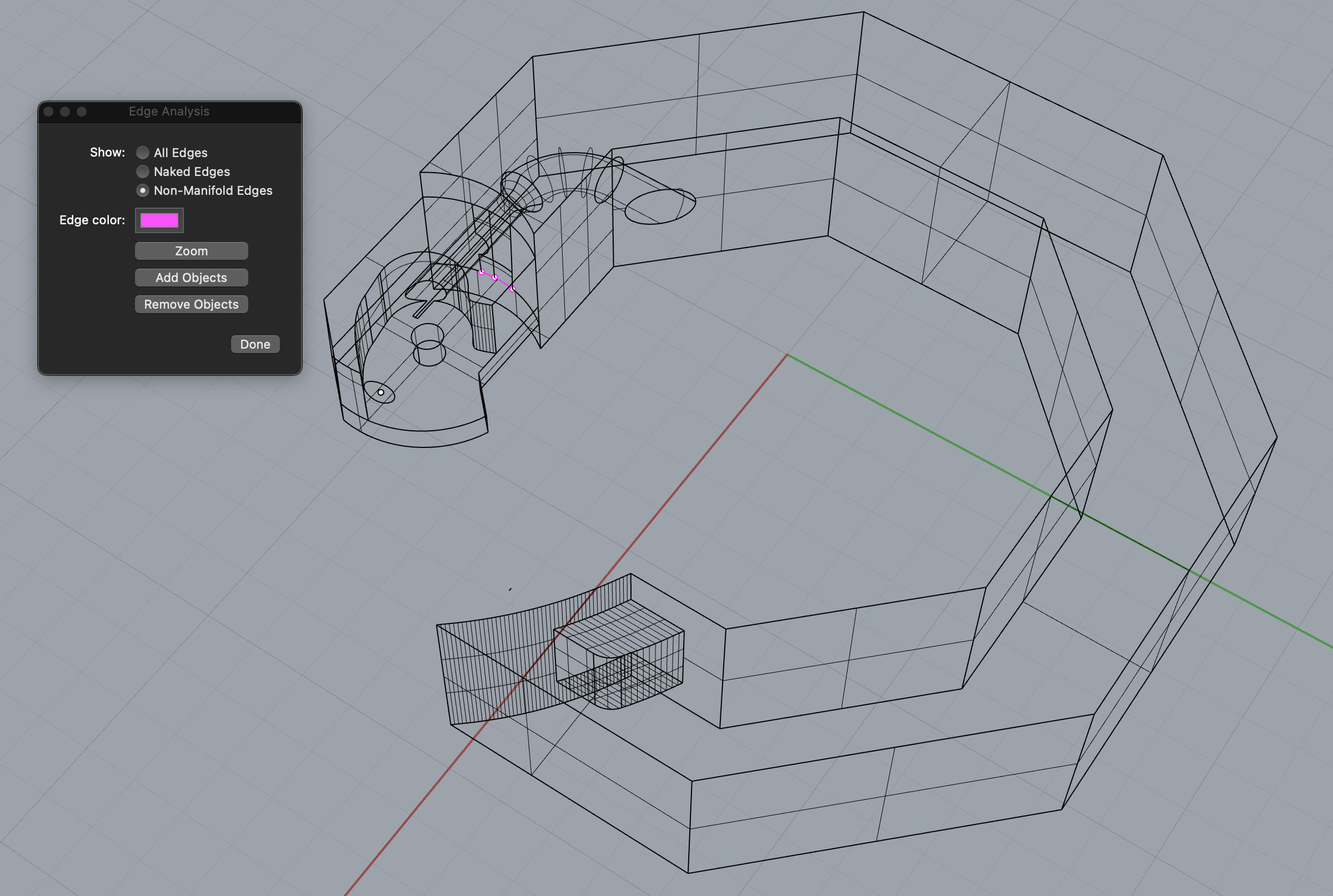
Image: discourse.mcneel.com
Tools and Plugins for Enhanced Edge Management
To further bolster your non-manifold edge-fighting arsenal, we recommend the following tools and plugins:
- Rhino’s QuadRemesh Plugin: This tool can automatically generate quad-dominant meshes, which tend to be free from non-manifold edges.
- Meshmixer’s Make Manifold Tool: Meshmixer offers a powerful “Make Manifold” tool that can resolve non-manifold issues with impressive precision.
- Blender’s EdgeTools Addon: Blender users can leverage this addon to detect and fix non-manifold edges, along with a host of other edge-related operations.
How To Fix Non Manifold Edges Rhino
Conclusion
Non-manifold edges may seem like formidable foes, but with the knowledge and tools provided in this guide, you now have the power to vanquish them from your Rhino models. Remember, the key to success lies in meticulous modeling practices and a persistent pursuit of clean and manifold geometry.
By embracing the advice of experts and utilizing the recommended tools, you can conquer the challenges of non-manifold edges, ensuring the health and integrity of your 3D creations. Now, go forth and unleash your modeling prowess!







